In today’s digital age, screens are everywhere, and they’ve become a significant part of our daily lives. As a parent or caregiver, you might wonder how this constant exposure affects young children.
The impact of screen time on early childhood development is a topic that’s gaining more attention, and for good reason. Research shows that excessive screen time can influence cognitive, social, and emotional growth in little ones. It’s not just about the hours spent in front of a screen; it’s also about the content consumed and the way it replaces crucial hands-on experiences.
Understanding these effects can help us make informed choices that nurture healthy development in our children.
Understanding Screen Time
Screen time refers to the amount of time children spend in front of screens, including TVs, computers, tablets, and smartphones. It encompasses both passive viewing and interactive engagement with digital content.
Definition of Screen Time
Screen time includes various activities that involve the use of electronic devices. Definitions often categorize screen time into two main types: recreational and educational. Recreational screen time involves leisure activities, like playing video games or watching shows.
Educational screen time includes learning-based applications and programs designed to enhance cognitive skills. Understanding these distinctions helps evaluate the impact of screen time on young children’s development.
Types of Screen Time
- Passive Screen Time: This involves watching videos or shows without interaction, potentially leading to reduced engagement and critical thinking skills.
- Interactive Screen Time: This consists of games and apps requiring user input, encouraging problem-solving and creativity.
- Educational Content: Programs and applications designed for learning enhance language skills, numeracy, and social awareness.
- Social Interaction: This includes video calls and messaging applications, promoting communication skills and emotional connections with peers and family.
- Unmonitored Screen Time: This type lacks oversight, increasing the risks of exposure to inappropriate content or excessive duration.
Grasping these categories aids parents in making informed choices regarding screen exposure and content appropriateness, contributing to healthier developmental practices.
Positive Effects of Screen Time
Screen time can offer various benefits for early childhood development when used appropriately. Understanding these positive aspects allows parents to harness technology effectively.
Educational Apps and Programs
Educational apps and programs foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills. They engage children with interactive content tailored to different age groups. For instance, programs like ABCmouse or Khan Academy Kids provide structured learning that enhances literacy and numeracy.
Research shows that children exposed to high-quality educational content demonstrate improved academic performance compared to peers with no access to such resources. Engaging activities in apps keep children motivated and encourage independent learning.
Social Interaction Opportunities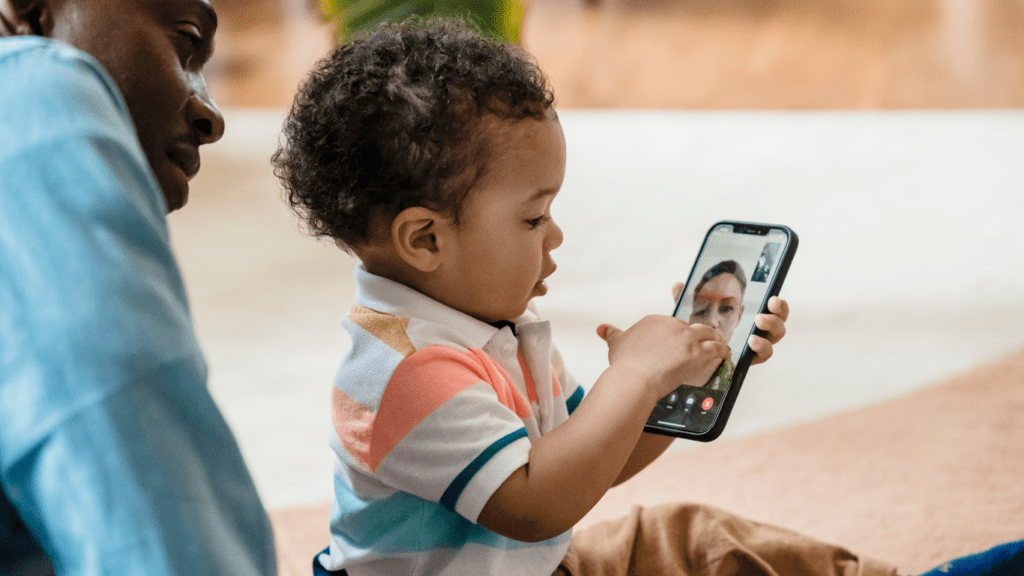
Screen time also facilitates social interaction among young children. Video calls and social media platforms enable them to connect with family members and friends, fostering relationships even from a distance.
Engaging in group activities on multiplayer games encourages collaboration and teamwork. Studies indicate that social engagement through screens can enhance emotional intelligence and empathy, as children learn to navigate social cues in virtual settings.
Negative Effects of Screen Time
Excessive screen time poses various risks to children’s growth and development. My focus here is on cognitive development concerns and the impact on physical health.
Cognitive Development Concerns
Cognitive development suffers from excessive screen exposure. Studies show that prolonged screen time correlates with attention problems, lower academic performance, and diminished language skills (American Academy of Pediatrics, 2016).
Children engaged in passive content, like television, often miss critical interactions that boost vocabulary and comprehension. Limited engagement with real-world stimuli restricts imaginative play and creative thinking in young minds.
Also, children may find it harder to concentrate and perform tasks effectively when they’ve spent too much time in front of screens.
Impact on Physical Health
Physical health is negatively impacted by excessive screen time as well. Increased sedentary behavior contributes to obesity and poor cardiovascular health in children. Research indicates that children engaging in more than two hours of screen time daily show higher rates of obesity due to lack of physical activity (National Institutes of Health, 2020).
Poor posture during screen use can result in musculoskeletal issues, including neck and back pain. Additionally, extended screen exposure leads to eye strain, commonly referred to as digital eye strain, resulting in discomfort and long-term vision problems.
Recommendations for Screen Time Management
Managing screen time effectively influences early childhood development significantly. Establishing clear guidelines helps ensure that children’s screen exposure is beneficial rather than detrimental.
Age-Appropriate Guidelines
I recommend adhering to age-appropriate guidelines for screen time to promote healthy habits. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) suggests:
- Under 18 months: Avoid screen use, except for video chatting.
- 18 to 24 months: Introduce high-quality educational programming. Parents should co-view to enhance understanding.
- 2 to 5 years: Limit screen time to one hour of high-quality content daily. Co-viewing continues to support learning.
- 6 years and older: Set consistent limits on screen time. Encourage activities that promote balance, including physical activity and unstructured play.
Implementing these guidelines ensures that children benefit from screens without excessive exposure.
Creating a Balanced Media Diet
I find that creating a balanced media diet is essential for supporting children’s overall development. This approach includes:
- Diverse content: Encourage varied genres, mixing educational, creative, and interactive programs. Ensure content promotes critical thinking and imagination.
- Interactive involvement: Engage with children during screen time. Discuss content, ask questions, and relate it to their experiences for deeper comprehension.
- Unscreened time: Prioritize alternative activities, focusing on outdoor play, reading, and family interactions to foster a well-rounded development.
By combining different media types and encouraging active engagement, screen time becomes a supportive tool in a child’s development journey.