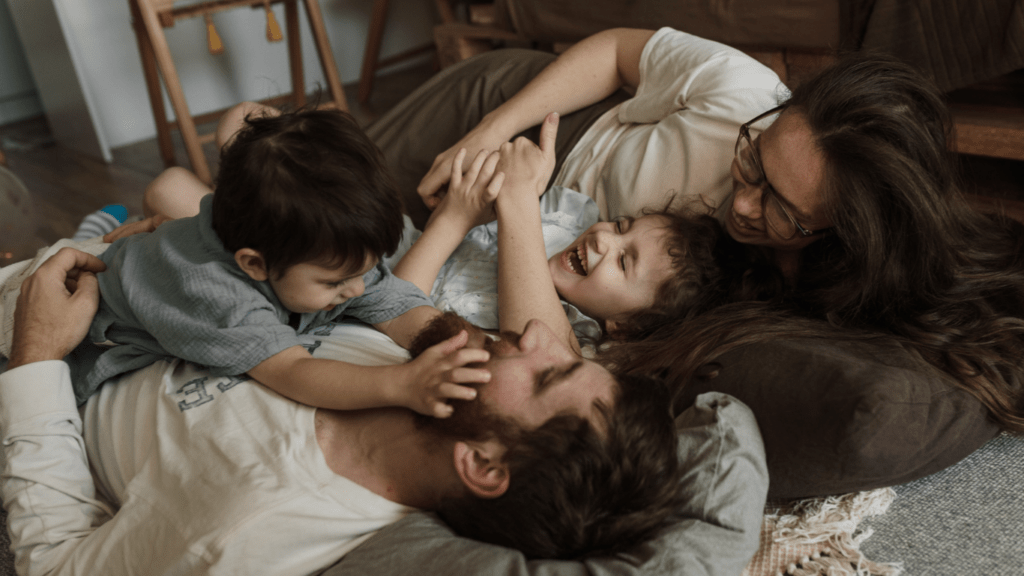
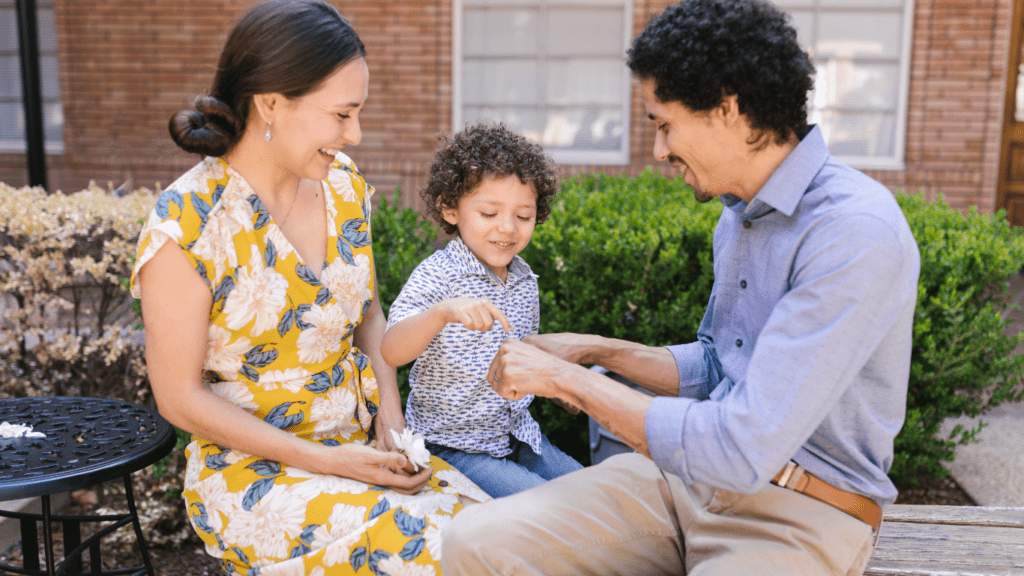
From the moment a child enters the world, the bond they form with their parents shapes their emotional landscape. I’ve always been fascinated by how these early connections lay the groundwork for a child’s future relationships and emotional well-being.
Parental bonding isn’t just about love and affection; it’s a critical component of emotional growth that influences everything from social skills to resilience. Research shows that strong parental bonds can significantly impact a child’s ability to navigate their feelings and build healthy relationships later in life.
As I delve into this topic, I’ll explore how nurturing interactions during those formative years can foster emotional intelligence and stability. Understanding this connection can empower parents to create a supportive environment that nurtures their child’s emotional development.
The Role of Parental Bonding in Early Emotional Growth
Parental bonding significantly influences early emotional growth. It establishes a foundation for emotional intelligence, resilience, and social skills. Secure attachments formed through consistent care, nurturing, and responsiveness set the stage for healthy emotional development.
Parental responsiveness impacts children’s emotional regulation. When parents respond appropriately to their child’s needs, it teaches them to manage their emotions effectively. For instance, a parent comforting a crying infant helps develop a sense of security, allowing the child to understand and express emotions gradually.
Positive interactions foster self-esteem and confidence. Engaging in activities like play, reading, and conversation promotes a child’s sense of worthiness. Children who experience supportive interactions tend to show better social competence and communication skills.
Nurturing behaviors also encourage empathy. When parents model empathetic responses, children learn to recognize and understand others’ emotions. An example includes acknowledging a friend’s feelings after a disappointing event, demonstrating compassion and support.
Secure attachment relationships contribute to long-term emotional well-being. Study findings indicate that children with strong parental bonds are less likely to experience anxiety or depression later in life.
These children often develop trusting relationships throughout adulthood, enhancing interpersonal connections. Overall, parental bonding plays a vital role in shaping a child’s emotional landscape.
For parents, consistent nurturing practices create a supportive environment crucial for their child’s emotional and social development.
Importance of Parental Bonding
Parental bonding significantly impacts a child’s emotional growth. The connection established from birth lays the groundwork for emotional security and trust, essential for healthy development.
Emotional Security
Emotional security emerges from strong parental bonds. Children feel protected when parents consistently respond to their needs. This sense of safety allows them to explore their environment and express emotions freely.
Secure attachments foster resilience, enabling children to navigate challenges effectively. Studies show that emotionally secure children demonstrate higher levels of emotional regulation and less anxiety (American Psychological Association, 2021).
Trust Development
Trust development relies heavily on parental bonding. When parents provide reliable support, children learn to trust not only their caregivers but also themselves and others. Consistent nurturing actions, like reassuring words during distress, cultivate a belief that their needs matter.
Research indicates that children with trustworthy parental relationships are more likely to form healthy friendships and collaborations later in life (Child Development Journal, 2022). These foundational trust-building experiences shape their interactions throughout adulthood.
The Impact on Child Development
Parental bonding significantly influences various aspects of a child’s development, particularly cognitive growth and social skills. Early interactions shape foundational abilities essential for lifelong success.
- Cognitive Growth:
Parental involvement directly stimulates cognitive development. Engaging in activities like reading and problem-solving expands a child’s understanding and critical thinking skills. Research indicates that children with strong parental bonds show improved memory, language acquisition, and attention span.
- Social Skills:
Parental bonding plays a vital role in developing social skills. Insecure attachments can lead to difficulties in forming relationships. Children who experience responsive parenting learn to share, cooperate, and communicate effectively.
Factors Influencing Parental Bonding
Parental bonding is influenced by various factors that shape the nature of the relationship between parents and their children. Understanding these factors helps in fostering stronger connections and promoting emotional growth.
Parenting Styles
Parenting styles significantly impact the quality of parental bonding. Authoritative parenting, characterized by warmth and structure, promotes secure attachments. This style encourages open communication and supports children’s independence.
In contrast, authoritarian parenting, with its rigid rules and lack of warmth, can hinder emotional connection. Permissive parenting often leads to a lack of boundaries, resulting in less effective parental guidance. Each style shapes children’s emotional regulation and self-esteem, thereby influencing their ability to form healthy relationships in the future.
Cultural Variations
Cultural variations also play a crucial role in parental bonding. Different cultures prioritize various aspects of parenting, impacting attachment styles. Collectivist cultures often emphasize familial interdependence and communal values, fostering strong family bonds.
Individualist cultures may promote independence, shaping attachment through different expectations. These cultural contexts dictate how parents engage with their children, influencing emotional security and developmental outcomes.
Understanding these variations is essential for appreciating the diverse experiences that shape parental bonding and its impact on children’s emotional growth.
Long-Term Effects of Bonding
Parental bonding significantly impacts children’s mental health and relationship patterns throughout their lives. Early emotional connections shape future well-being and social dynamics.
Mental Health Outcomes
Children with secure attachments to their parents exhibit lower rates of anxiety and depression in adolescence and adulthood. Research shows that these individuals are better equipped to cope with stress and emotional challenges.
Consistent nurturing from parents fosters resilience, equipping children to handle life’s pressures effectively. Securely attached children often demonstrate higher self-esteem, leading to a more positive self-image.
Studies indicate that emotional security gained from bonding translates into healthier coping mechanisms, reducing vulnerability to mental health disorders later in life.
Relationship Patterns
Bonding influences how children form relationships as adults. Secure attachments encourage healthy interpersonal behaviors, such as trust and open communication. These children tend to develop fulfilling friendships and romantic partnerships rooted in mutual respect and empathy.
Conversely, insecurely attached individuals may struggle with intimacy and exhibit patterns of avoidance or dependency in relationships. Research highlights that strong family connections promote effective conflict resolution skills, allowing for healthier interpersonal dynamics.
Overall, parental bonding serves as a blueprint for future relational success and emotional intimacy.