As a parent, I often find myself worried about my child’s health and well-being. One crucial aspect that often gets overlooked is indoor air quality. It plays a significant role in child development, impacting everything from cognitive function to physical health.
With kids spending most of their time indoors, the air they breathe can greatly influence their growth and learning abilities. Poor indoor air quality can lead to a range of issues, including respiratory problems and developmental delays.
Understanding this connection can empower us to create healthier environments for our little ones. In this article, I’ll explore the importance of maintaining good air quality at home and share practical tips to ensure our children breathe easier and thrive.
The Importance of Indoor Air Quality in Child Development
Indoor air quality significantly influences child development. Exposure to pollutants can impair cognitive functions, leading to learning difficulties. Research shows that children in environments with high levels of allergens and pollutants experience more frequent respiratory issues, which affects their ability to focus and learn.
Poor air quality can stem from various sources, such as mold, dust, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released from household products. These contaminants irritate the respiratory system and can contribute to developmental delays.
For instance, studies indicate that children exposed to high levels of indoor air pollutants have lower performance on standardized tests. Maintaining optimal indoor air quality supports physical health and cognitive function.
Regularly ventilating living spaces minimizes pollutant concentrations. Utilizing air purifiers with HEPA filters effectively reduces airborne particles, creating a healthier environment. It’s essential to monitor humidity levels, as excessive moisture encourages mold growth, which poses health risks.
Involving children in discussions about air quality encourages awareness and promotes healthy habits early on. Teaching them about the significance of clean air fosters long-term appreciation for their environment.
By prioritizing air quality, parents can contribute to healthier development and improved overall well-being for their children.
Key Factors Affecting Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality significantly impacts children’s health and development. Various factors contribute to air quality, and understanding them is crucial for maintaining a healthy environment.
Common Indoor Pollutants
Indoor spaces often contain pollutants that adversely affect air quality. These common pollutants include:
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Found in paints, varnishes, and cleaning products, VOCs can lead to respiratory issues and cognitive impairments.
- Particulate Matter (PM): Tiny particles from dust and pet dander can contribute to allergies and asthma-related problems.
- Mold Spores: Mold thrives in damp areas and releases spores that can irritate the respiratory system and trigger allergic reactions.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): High levels of CO2 can result from inadequate ventilation, leading to fatigue and reduced cognitive function.
- Formaldehyde: Present in furniture and building materials, formaldehyde exposure can cause irritation and long-term health issues.
Sources of Air Pollution in Homes
Identifying sources of indoor air pollution helps in creating a healthier environment. Key sources include:
- Cooking Appliances: Gas stoves and ovens can emit nitrogen dioxide and other harmful gases if not properly ventilated.
- Heating Systems: Furnaces and space heaters may release pollutants if not maintained routinely.
- Household Products: Cleaning supplies, air fresheners, and personal care products often contain harmful chemicals.
- Building Materials: Certain flooring, insulation, and furniture materials can off-gas harmful substances over time.
- Outdoor Air: Pollutants from outside, like vehicle emissions, can infiltrate homes through windows and doors, affecting indoor air quality.
By staying informed about these factors, parents can take proactive steps to improve the air quality in their homes, promoting better health and development for their children.
Impact of Indoor Air Quality on Health
Indoor air quality significantly affects children’s health. Poor air can lead to immediate and lasting health issues.
Short-Term Health Effects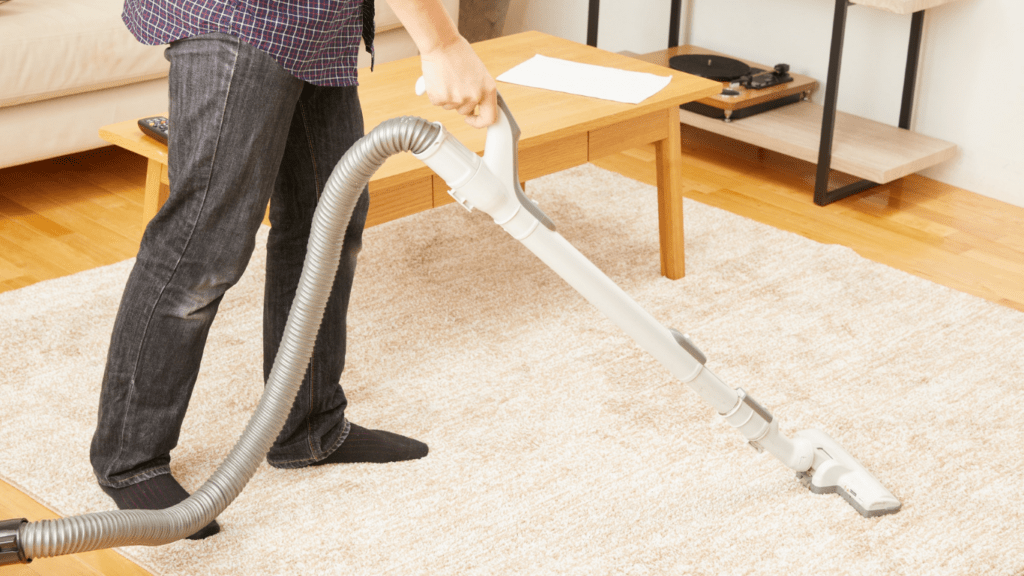
Short-term exposure to indoor air pollutants often results in respiratory problems. Symptoms include coughing, sneezing, and shortness of breath. Children may experience headaches, fatigue, and irritability, which can disrupt their daily activities and learning.
Allergens like dust mites and mold spores exacerbate these conditions, leading to increased absenteeism from school and decreased concentration.
Long-Term Health Consequences
Long-term exposure to poor indoor air quality poses serious health risks. Research links chronic exposure to pollutants with the development of asthma, allergies, and other respiratory diseases.
Cognitive impairments may arise from pollutants like volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which affect memory and learning abilities. Moreover, children who grow up in environments with persistent indoor air issues may face developmental delays and difficulty in academic performance.
Indoor Air Quality and Cognitive Development
Indoor air quality significantly impacts cognitive development in children. Exposure to pollutants can hinder their learning abilities and concentration levels.
Influence on Learning and Concentration
Pollutants in the air can affect children’s cognitive functions. Research shows that elevated levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter (PM) correlate with decreased attention spans and lower academic performance.
A study by the Environmental Protection Agency indicates that children exposed to high CO2 levels struggle with problem-solving and critical thinking, essential skills for successful learning. Ensuring clean air in learning environments helps improve focus and enhances overall educational outcomes.
Effects on Behavioral Health
Poor indoor air quality also links to behavioral issues in children. Exposure to allergens and irritants can increase anxiety and irritability, influencing mood and social interactions.
The World Health Organization reports that children in homes with high levels of indoor pollutants face a higher risk of developing attention disorders. Maintaining good indoor air quality can contribute to improved emotional regulation, fostering a supportive atmosphere for healthy child development.
Strategies to Improve Indoor Air Quality
Improving indoor air quality significantly enhances children’s health and development. Implementing effective strategies can help create a cleaner, safer environment for kids.
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance and cleaning help reduce indoor pollutants.
- Dusting surfaces: I dust surfaces weekly to minimize dust and allergens.
- Vacuuming carpets: I vacuum carpets and rugs at least twice a week using a vacuum equipped with a HEPA filter to trap small particles.
- Washing bedding: I wash bedding and curtains in hot water monthly to eliminate dust mites and allergens.
- Changing HVAC filters: I replace air filters in heating and cooling systems every three months to optimize airflow and reduce contaminants.
- Checking for mold: I inspect areas prone to moisture, like bathrooms and kitchens, for mold growth and address any issues promptly.
Use of Air Purifiers and Ventilation
Using air purifiers and ensuring proper ventilation improve air quality indoors.
- Selecting air purifiers: I choose air purifiers with HEPA filters to remove fine particles and allergens.
- Positioning purifiers: I place purifiers in key areas, such as bedrooms and playrooms, for maximum efficiency.
- Opening windows: I open windows whenever outdoor air quality is good to allow fresh air exchange and reduce indoor pollutants.
- Using exhaust fans: I run exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms to eliminate moisture and odors, which can lead to mold growth.
- Monitoring CO2 levels: I utilize carbon dioxide monitors to ensure adequate ventilation, especially in high-usage areas like classrooms and playrooms.
By implementing these strategies, I contribute to a healthier indoor environment that supports my children’s development.